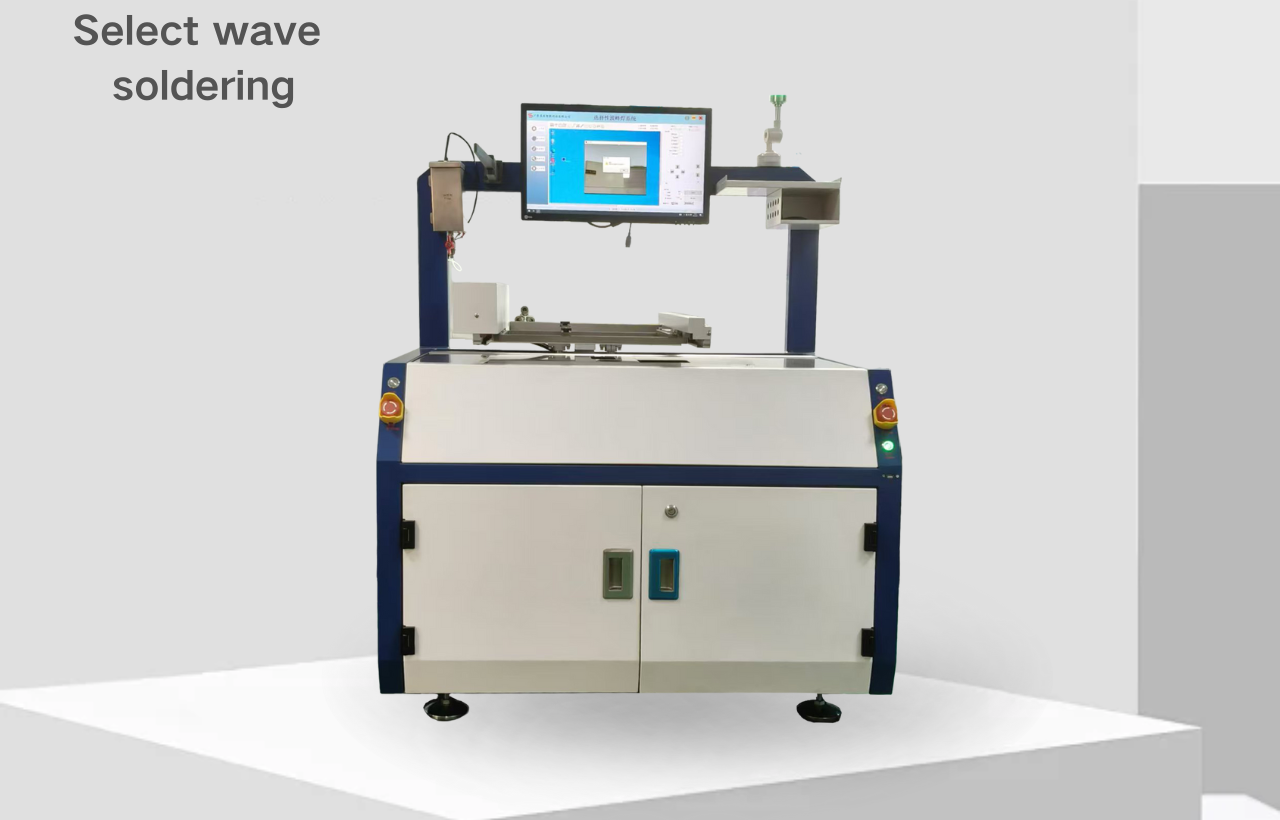
Selective soldering is a localized soldering process used in the post-SMT assembly stage. It is used for precisely soldering solder joints on PCBs that are unsuitable for wave soldering or reflow soldering (such as through-hole components, irregularly shaped components, and areas around heat-sensitive components), offering both flexibility and reliability.
Key Process Steps:
Flux Application: Flux is precisely sprayed onto the target solder joints through a nozzle, wetting only the areas to be soldered.
Preheating: The PCB is locally preheated to activate the flux and prevent thermal shock during soldering.
Dip Soldering / Drag Soldering: The solder nozzle rises, allowing the solder to wet the solder joints; or the PCB moves, dragging the solder joints across the nozzle surface to form full solder joints.
Cooling: The solder joints are cooled naturally or forcibly to ensure a stable crystal structure.

-
Wave soldering output conveyor QJ400-BO
-
Benchtop Manual Smt Frameless PCB Solder Paste Stencil Printer Printing Machine
-
SMT Manual Frameless Pcb Solder Paste Stencil Printer
-
SMT frameless steel stencil screen printing table
-
Nitrogen generator, used for selective welding
-
Desktop selection welding QSO-300B
-
Desktop Selective Wave Soldering Machine QH-SHSS341
-
SMT semi-automatic pick and place machine with Dispenser
-
SMT X-Ray Intelligent Item Counting Machine









