Author:Zhou
For quite some time, the industry has not been sufficiently aware of the cleaning process. Mainly because of the former PCBA assembly density is low, flux residues and other contaminants on the electrical performance of the adverse effects are not easy to be detected. Nowadays, as the design of PCBA develops towards miniaturisation, the size of devices and the spacing between devices become smaller, and failure malfunctions such as short-circuits and electrochemical migration caused by tiny particles residues have attracted widespread attention. In order to adapt to the market trend and improve the reliability of products, more and more SMT manufacturers have started a journey to seek knowledge about the cleaning process.
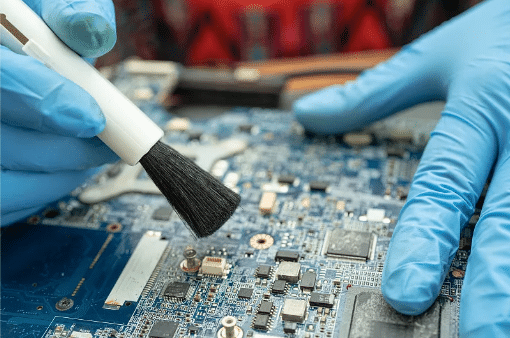
Cleaning process that combines the static cleaning power of the cleaning agent and cleaning equipment dynamic cleaning power, and ultimately the removal of pollutants in the process. pcba cleaning is divided into SMD (SMT) and plug-in (THT) two phases, through the cleaning of the product in the processing of surface contaminants can be removed in the process of the accumulation of pollutants, reduce the product by the surface contamination and the risk of reducing the reliability of the product. In the electronics manufacturing and semiconductor processing industry, it is very important to choose the right cleaning agent with the appropriate cleaning equipment. Factors affecting the stability of the PCBA cleaning process mainly include: cleaning objects, cleaning equipment, cleaning agents and process control.
Cleaning object
The object of cleaning in general is solder paste and flux residues, which cause electrochemical migration, corrosion and short-circuiting, posing a great threat to product reliability, although large particles of contamination, grease and perspiration on the surface of the circuit boards cannot be ruled out. Different PCBA material properties and surface conditions are also different. In many cases the customer’s products cannot be exposed to water and therefore are not suitable for the immersion cleaning process. There are also some components that are made up of sensitive metals that are very fragile and cannot be cleaned using ultrasonic waves or those bubbles will shatter the components when they explode. There are also components that must be ‘gently’ treated with pH-neutral cleaning solutions! Often circuit boards have very complex geometries on their surfaces and very high integration densities. When the distance between the device and the substrate is very small, deionised water droplets will not be able to drill into the small gaps, and will not be able to remove the contaminants at the bottom of the device, which will require chemical cleaners to help.
Cleaning agent
It is very important to choose specialised cleaning agents. Cleaning fluids, as a chemical used on production lines and which may come into direct contact with the human body, carry the risk of personal injury and economic loss caused by improper handling. Material compatibility is an often overlooked but crucial part of the cleaning process. For example, power module packages with various metallic materials such as copper, nickel or aluminium are susceptible to corrosion or oxidation of aluminium chips and copper surfaces, and in some cases character removal, as a result of improper cleaning processes. Therefore, the incompatibility of materials between the cleaning agent and the cleaning object, and between the cleaning agent and the cleaning equipment may lead to product obsolescence, or cause clogging of the equipment pipeline.
Cleaning equipment
A complete cleaning process usually consists of washing, rinsing and drying, in which the cleaning agent and the contaminants come into contact with each other and the cleaning agent separates the contaminants from the surface of the object to be cleaned, while the rinsing and drying processes further remove the contaminants and make sure that there is no residue of the cleaning agent on the surface of the components.
Cleaning process control
As the cleaning time increases, the contaminants that continue to enter the cleaning fluid will have a negative impact on cleaning efficiency. When should I change the fluid? When is the latest fluid change? How do I adjust cleaning parameters when the environment/product changes? These questions are directly related to the customer’s cost and output, and the key to finding the answer lies in the collection of cleaning data, including: time, action, concentration and temperature. Which cleaning fluid in the use of the process will be affected by a number of factors, such as: residues in the liquid, liquid evaporation, deionised water added, etc., its concentration will often fluctuate. Therefore, in the circuit cleaning process, the concentration of the monitoring is directly related to the stability of the cleaning effect.

1 Comment
I just could not leave your website prior to suggesting that I extremely enjoyed the usual info an individual provide on your guests?
Is going to be again steadily in order to check out new posts!